
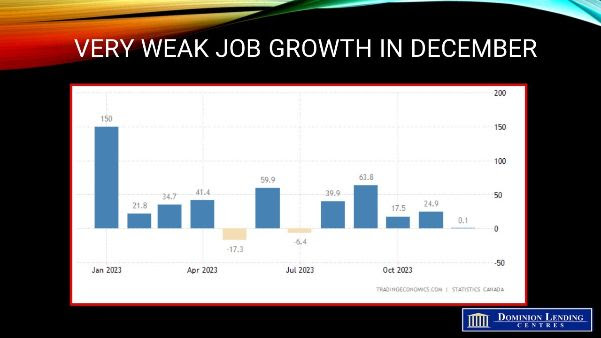
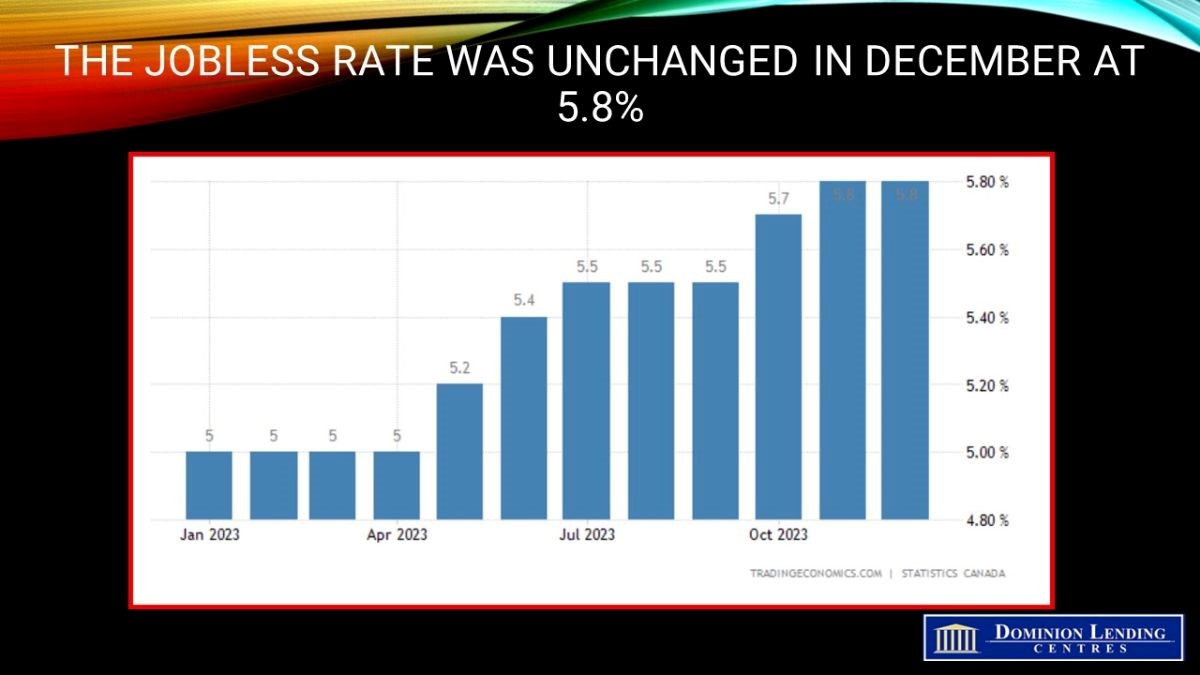
Today’s StatsCanada Labour Force Survey for December was a mixed bag and far more robust than the weak headline figure suggests. Total employment in Canada barely budged, rising by a mere 100 jobs in the final month of last year. However, the labour force participation rate fell, leaving the unemployment rate at 5.8%. Most economists had been expecting considerably more robust job growth and a rising unemployment rate.
Canada has one of the world’s fastest-growing populations owing to high immigration levels. However, employment growth has been slower than labour force growth in recent months.
The employment rate–the proportion of the working-age population with jobs–trended downward in 2023 among core-aged men and women (aged 25 to 54).
The participation rate—the number of employed and unemployed people as a percentage of the population aged 15 and older—fell in December (-0.2 percentage points) to 65.4%. This was down from a recent peak of 65.7% in June. Most of the decline from June to December was attributable to a drop in the youth participation rate, which decreased 2.1 percentage points to 63.5% over the period. On a year-over-year basis, the labour force participation rate fell 3.3 percentage points to 85.4% among youth not attending school. At the same time, it declined 1.0 percentage points to 46.4% among youth who were students (not seasonally adjusted).

The participation rate held steady among those in the core-aged group (88.7%) and people aged 55 years and older (36.9%), compared with June 2023 and December 2022.
Total hours worked rose 0.4% month-over-month in December and 1.7% from a year earlier. That followed a 0.7% month-over-month drop in November.
Employment in professional, scientific and technical services increased by 46,000 (+2.4%) in December, following little change in the three previous months. This was the second monthly increase in the industry in 2023, the first having been a rise of 52,000 in August. On a year-over-year basis, employment in this industry was up by 78,000 (+4.2%) in December.
Following four months of little change, employment in health care and social assistance rose by 16,000 (+0.6%) in December, building on increases in June (+21,000) and July (+25,000). On a year-over-year basis, health care and social assistance employment increased by 124,000 (+4.8%) in December. According to the most recent data from the Job Vacancy and Wage Survey, the job vacancy rate in healthcare and social assistance was 5.3% in October 2023, down from a peak of 6.3% in April but still the highest rate across all sectors.
In December, employment fell in wholesale and retail trade (-21,000; -0.7%) for a third consecutive month. From August to December, work in the industry decreased by 80,000 (-2.7%). This followed gains from December 2022 to August 2023, when employment increased by 108,000 (+3.7%).
Employment rose in British Columbia (+18,000; +0.6%), Nova Scotia (+6,300; +1.3%), Saskatchewan (+4,800; +0.8%), and Newfoundland and Labrador (+2,400; +1.0%) in December, while it declined in Ontario (-48,000; -0.6%). Employment in other provinces was primarily unchanged.

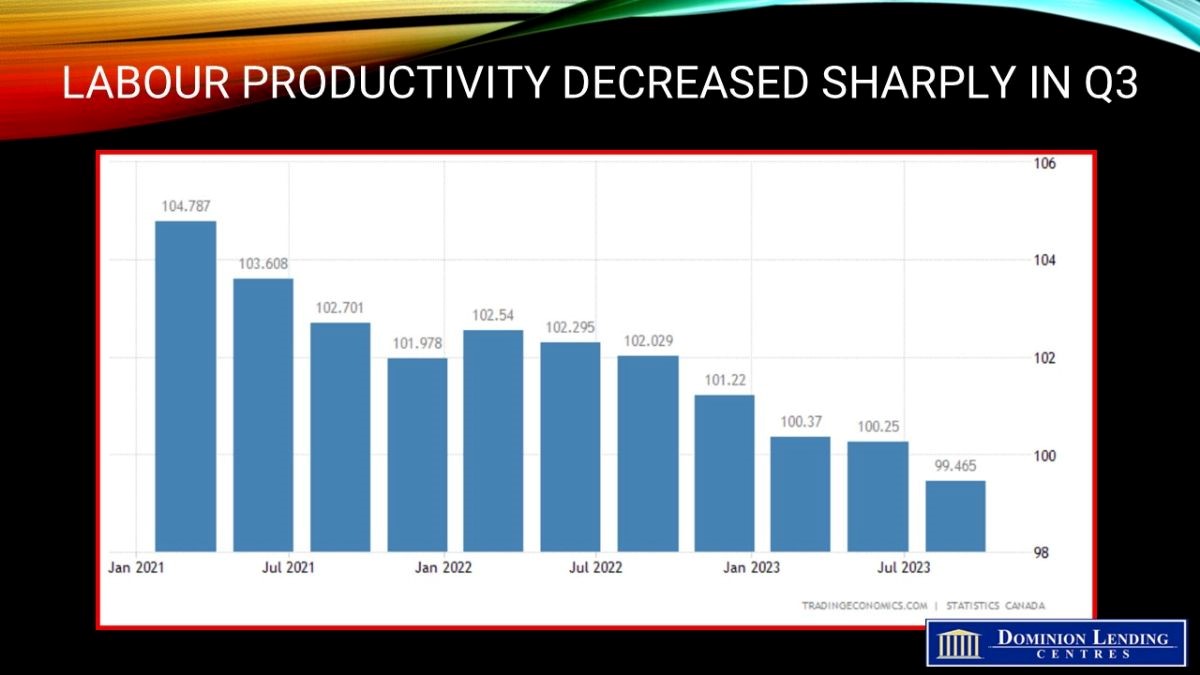
The most concerning thing for the Bank of Canada was the acceleration in wage inflation to 5.4% y/y last month, compared to 4.8% in the prior two months. With Canadian productivity falling, this is particularly troublesome for the overall inflation outlook. For this reason, the Bank of Canada will continue to be cautious.
Bottom Line
The next Bank of Canada confab is on January 24, before which we will see the December inflation data on January 16. Given the mixed labour force survey, particularly the wage spike, the Bank of Canada will remain cautious. They will wait until inflation is sustained meaningfully before 3% before cutting the overnight policy rate for the first time this cycle.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres