
|
|
|
Each Office Independently Owned & Operated
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

|
|
|
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

|
|
|
|
|
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

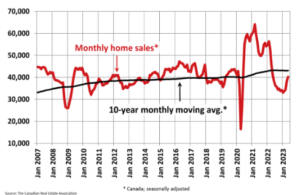
The Canadian Real Estate Association says home sales in May rose 5.1% month-over-month (m/m), adding to the 11.1% gain in April. This brought the year-over-year sales gain to 1.4%, The first y/y sales increase in almost two years. While spring home sales started booming (compared to the past year), the surprising 25 bps uptick in the Bank of Canada’s policy rate has no doubt dampened enthusiasm in June. Indeed, the strength in housing may have been the deciding factor in the Bank’s decision.
Sales were up in about 70% of all local markets, including Canada’s largest markets: the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), Montreal, Greater Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton, and Ottawa.
New Listings
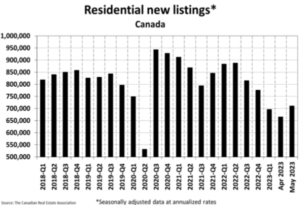
The number of newly listed homes was up 6.8% month-over-month in May, although the bigger picture is that new supply is still running at historically low levels.
With sales and new listings up by similar magnitudes in May, the sales-to-new listings ratio was 67.9%, little changed from 69% in April. The long-term average for this measure is 55.1%.
There were 3.1 months of inventory on a national basis at the end of May 2023, down from 3.3 months at the end of April and down more than an entire month from the most recent peak at the end of January. The long-term average for this measure is about five months.
The dearth of sellers could reflect the reluctance of existing homeowners to give up their low-rate mortgages.
Home Prices
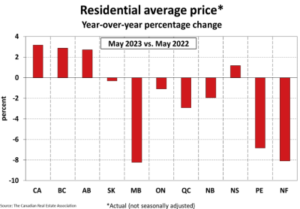
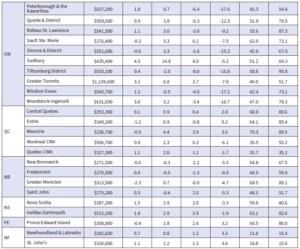
The Aggregate Composite MLS® Home Price Index (HPI) climbed 2.1% on a month-over-month basis in May 2023 – a significant increase for a single month and on the heels of a similar gain in April. Once again, it was also very broad-based, with a monthly price increase between April and May observed in most local markets.
The Aggregate Composite MLS® HPI now sits 8.6% below year-ago levels, a smaller decline than in the first four months of this year. The second chart below shows that year-over-year price gains are posted at the national level and in BC, Alberta, and Nova Scotia. With the strength in the GTA, y/y prices are fast approaching positive territory.


Bottom Line
The rate hike by the BoC has spooked the housing market. Anecdotal evidence suggests that activity has slowed, and the demand for fixed-rate mortgages has surged. Many households now face higher monthly payments in the next two years. The Bank of Canada knows that and wants to see household spending slow from the rapid Q1 pace. Consumer confidence has risen sharply since March. But with household debt-to-income levels at near-record highs, the sensitivity to interest rates is extreme.
Ironically, just as the BoC raised rates again after months of no action, the Federal Reserve decided to pause rate hikes for the first time this cycle. US inflation peaked at over 9.1% and fell to 4.0% in May. While Canadian inflation topped at 8.1%, its most recent posting was 4.4% in April. May data for Canada will be released on June 27.
Traders are currently expecting one more rate hike in Canada this year. The idea that the Bank would cut rates any time this year has vanished. Most are betting the first rate cut is more likely to be in mid-2024. We have learned that uncertainty prevails, but I’d bet that we will not return to pre-Covid interest rates for a very long time.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

The Canadian economy continues to show marked resilience to high-interest rates. Statistics Canada released data this morning showing real GDP rose at an above-consensus 3.1% annual rate in the first quarter of this year. The estimate for April growth was also firm, a harbinger of continued strength in Q2. The combined drags of the public sector strike and the Alberta wildfires didn’t cause a significant downdraft.
First-quarter growth was driven by strong international trade and robust household spending. These factors were partly mitigated by slower inventory accumulation and declines in new housing construction and business investment in machinery and equipment.
After two quarters of minimal growth, household spending rose for goods (+1.5%) and services (+1.3%) in the first quarter of 2023. Expenditures on durable goods (+3.3%) were driven by motor vehicles, including new trucks, vans, and sport utility vehicles (+7.8%). Spending on semi-durables (+4.3%) was led by garments (+4.5%), while spending on non-durable goods (-0.2%) declined slightly.
Service spending picked up in the first quarter of 2023, led by food and non-alcoholic beverage services (+4.4%), and alcoholic beverage services (+6.5%). Meanwhile, travel was on the rise, with expenditures by Canadians abroad up 6.8% in the first quarter, compared with a 3.3% decrease in the previous quarter.
These data do not portend a household sector overly burdened by rising mortgage and credit card payments.
Coinciding with higher borrowing costs and slowing mortgage borrowing, housing investment fell 3.9% in the first quarter of 2023, the fourth consecutive quarterly decrease. The decline in investment was widespread—as new construction (-6.0%), renovations (-2.1%), and ownership transfer costs (-1.5%), which represents resale activity, were all down.
We know housing activity has picked up considerably since the first quarter, undoubtedly adding to Q2 growth. Also expansionary is the persistent rise in employee compensation, led by salary gains in professional and personal services, manufacturing and construction.
One warning sign is the declining household savings rates and slower disposable income. Persistently high interest rates had a predominantly negative effect on net property income, as increases in interest income (+6.4%), mainly from deposits, did not keep pace with higher interest payments on mortgages (+14.7%) and consumer credit (+10.9%).
In contrast with lower disposable income, consumption expenditures (in nominal terms) rose 2.1% in the first quarter of 2023. This was faster than the 1.4% pace recorded in the fourth quarter of 2022, partly due to inflationary pressures. As a result, the household saving rate was 2.9% in the first quarter of 2023, down from 5.8% at the end of 2022. The household saving rate approached the pre-pandemic level, which averaged 2.1% in 2019.
Business incomes fell significantly in Q1, and judging from the stock market, corporate earnings news has also been disappointing across a wide array of sectors in the second quarter.
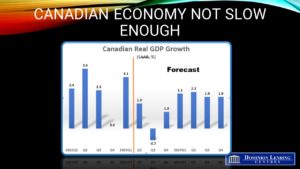
The strength in today’s data and the higher-than-expected inflation number for April will cause the Bank of Canada to seriously consider raising the overnight rate by 25 bps to 4.75% when they meet again next week. I think they will hold off to see the May employment and inflation data before they pull the trigger.
Markets have already responded to the numbers. Short-term interest rates remain well above levels posted earlier this year, although that is mainly about the debt-ceiling issue in the U.S. The Bank’s statement will undoubtedly be rather hawkish.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres
Posted by: Yen (Frank) Feng

The Canadian labour market has done it again, blowing past expectations for the fifth straight month. In April, a whopping 41,400 new jobs were added, more than double what economists predicted. Since February, monthly employment growth has averaged 33,000, following cumulative increases of 219,000 in December 2022 and January 2023.
The employment rate—the share of the population aged 15 and older—held steady at 62.4% for the third consecutive month in April. This is particularly noteworthy given the population grew by more than a million people in 2022 and is slated to snowball this year, thanks to immigration.
However, there is a catch. All the job growth in April was in part-time positions, while full-time jobs decreased by 6,200. But even with this slight hiccup, the labour market is still going strong, which means the Bank of Canada will likely continue its wait-and-see approach, even as we all wonder when the first rate cut will happen.
The jobless rate held steady at a near-record low of 5.0%, unchanged since December 2022. This remained near the record low of 4.9% observed in June and July 2022. Compared with April 2022, the unemployment rate was down 0.3 percentage points in April 2023.

Wage Inflation Remains High
Of great concern to the Bank of Canada, average hourly wages rose by 5.2% on a yearly basis in a further sign of the labour market’s resilience, with wage growth now above the annual rate of inflation, which was 4.3% in March. It is not that wage inflation caused the surge in the Consumer Price Index last year, but continued vigorous wage hikes become impended in wage-price spiralling as higher costs give businesses cover to rate prices.

Bottom Line
The BoC, despite this report, isn’t likely to budge from its current policy stance. As more and more immigrants enter the workforce, the traditional markers of a strong jobs report are evolving. Even though the unemployment rate remains steady at 5%, it may indicate that we’ve hit a new equilibrium point. That’s why this seemingly “surprising” report doesn’t hold the same weight as it would have in the past.
In addition, the BoC can quickly point out the narrowness of sector hiring and the trend of full-time employment declining while part-time jobs rise. After today’s release, the BoC’s decision to stay on the sidelines is a wise move. But it also means that the Bank will not be in a hurry to cut rates this year.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres