Odds of a Rate Cut Next Week Rise with Disappointed Canadian GDP Growth
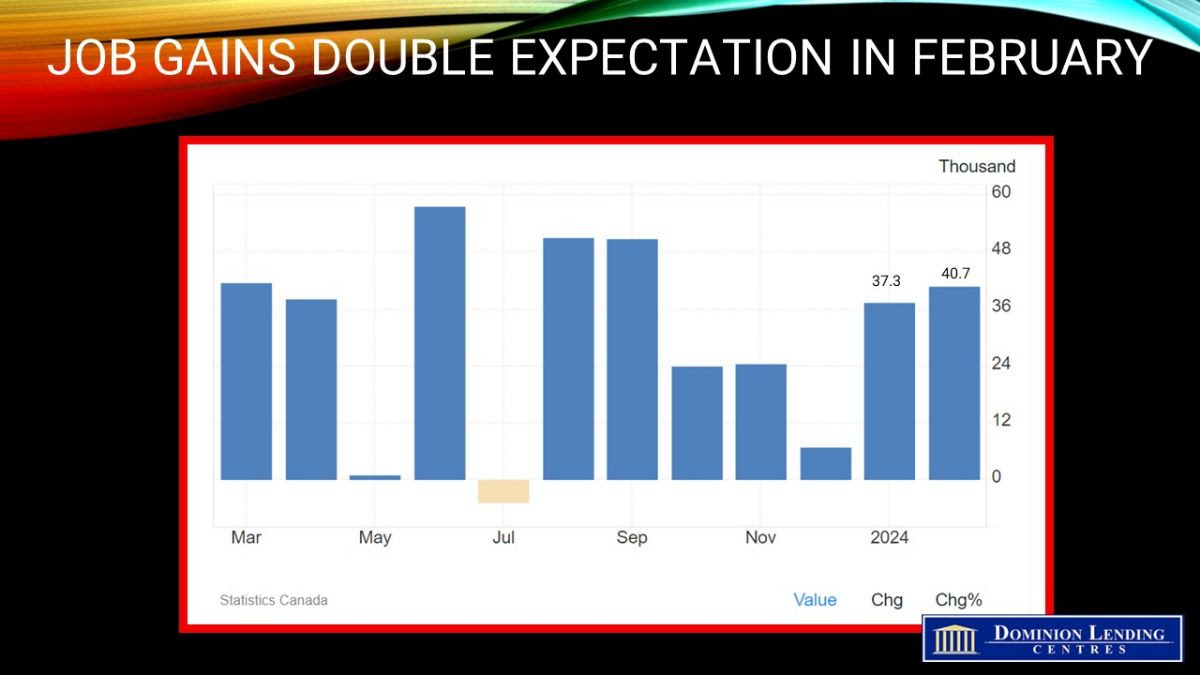
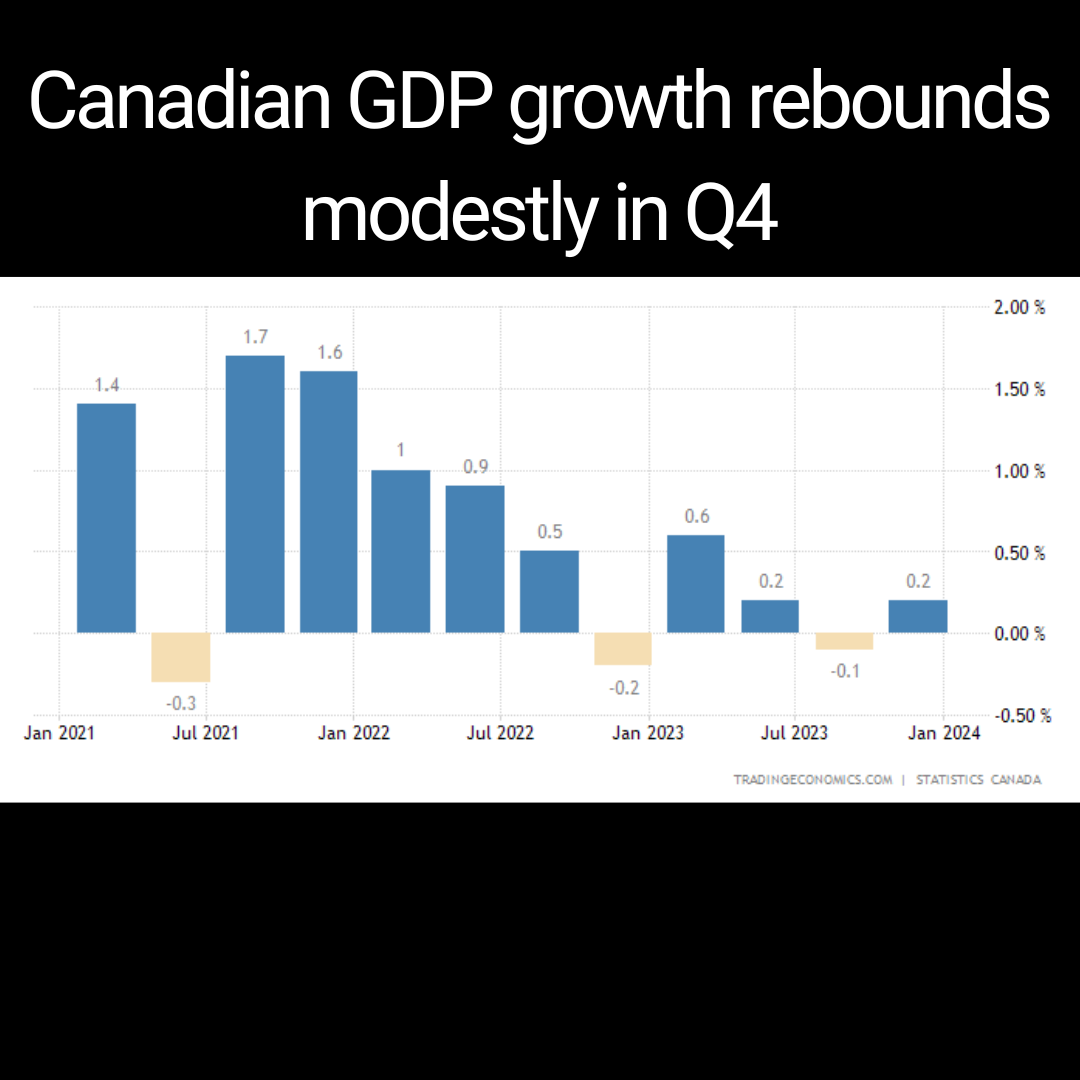
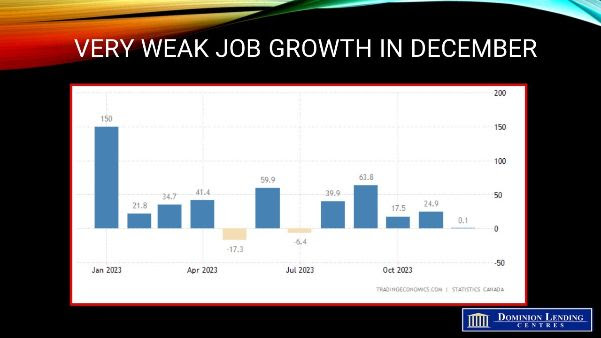
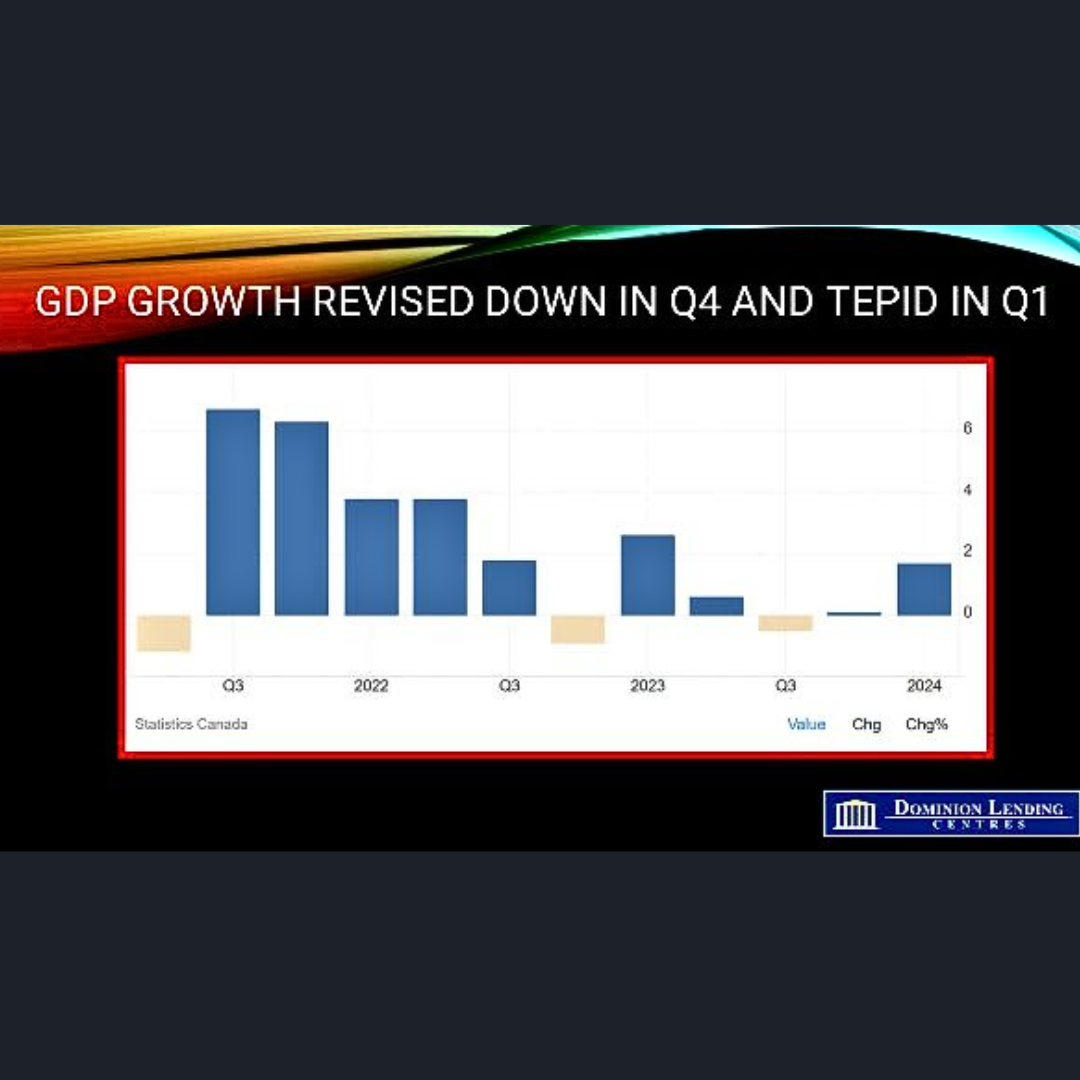
The likelihood of a rate cut next week has increased due to disappointing Canadian GDP growth. Real gross domestic product (GDP) only rose by 1.7% (seasonally adjusted annual rate) in the first quarter of this year, which is well below the expected 2.2% and the Bank of Canada’s forecast of 2.8%. Fourth-quarter economic growth was revised to just 0.1% from 1.0%. These figures have led traders to increase their bets on a Bank of Canada rate cut when they meet again next week.
In the first quarter of 2024, higher household spending on services—primarily telecom services, rent, and air transport—was the top contributor to the increase in GDP, while slower inventory accumulation moderated overall growth. Household spending on goods increased modestly, with higher expenditures on new trucks, vans and sport utility vehicles.
On a per capita basis, household final consumption expenditures rose moderately in the first quarter, following three-quarters of declines. Per capita spending on services increased, while per capita spending on goods fell for the 10th consecutive quarter.
Business capital investment rose in the first quarter, driven by increased spending on engineering structures, primarily within the oil and gas sector. Business investment in machinery and equipment also increased, coinciding with increased imports of industrial machinery, equipment and parts.
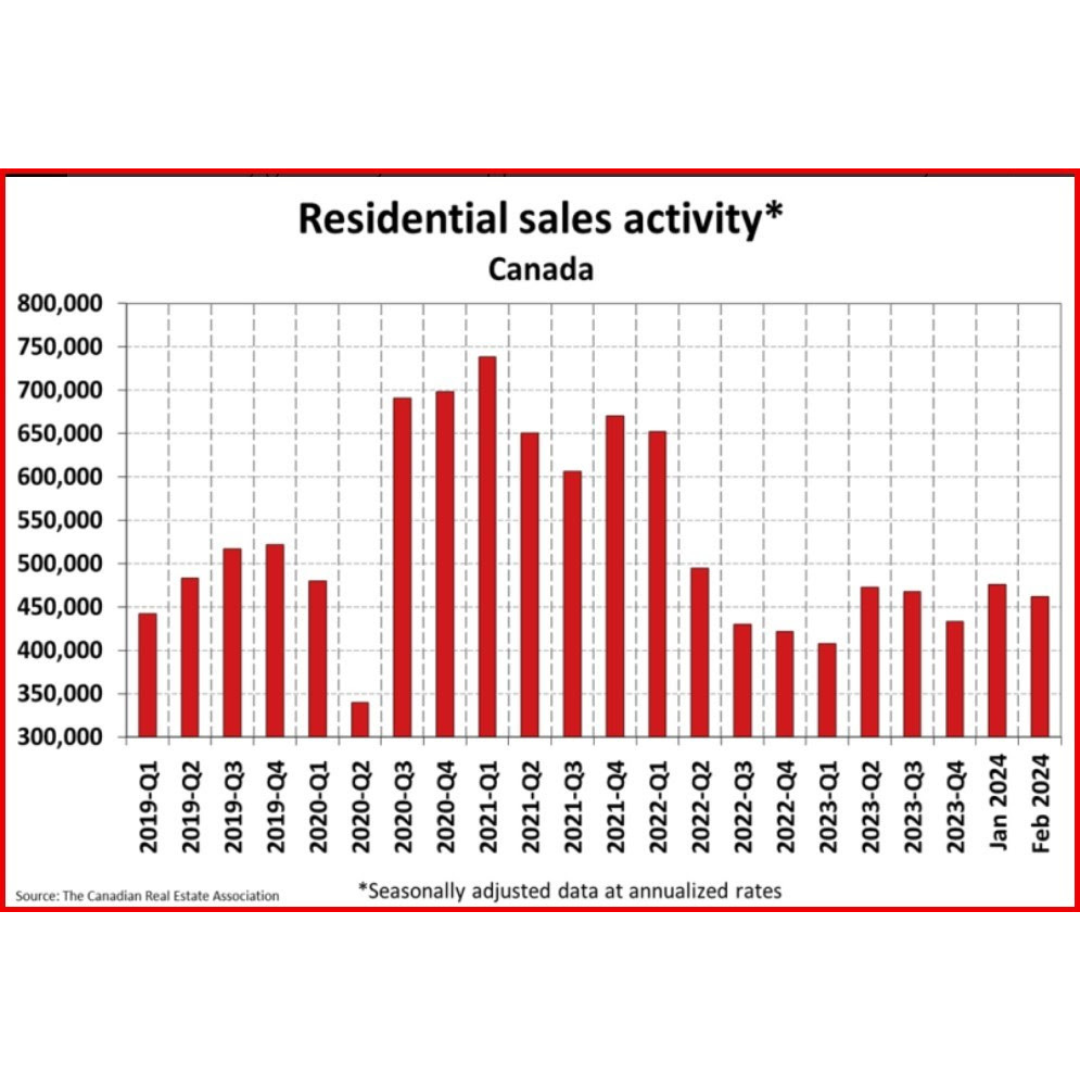
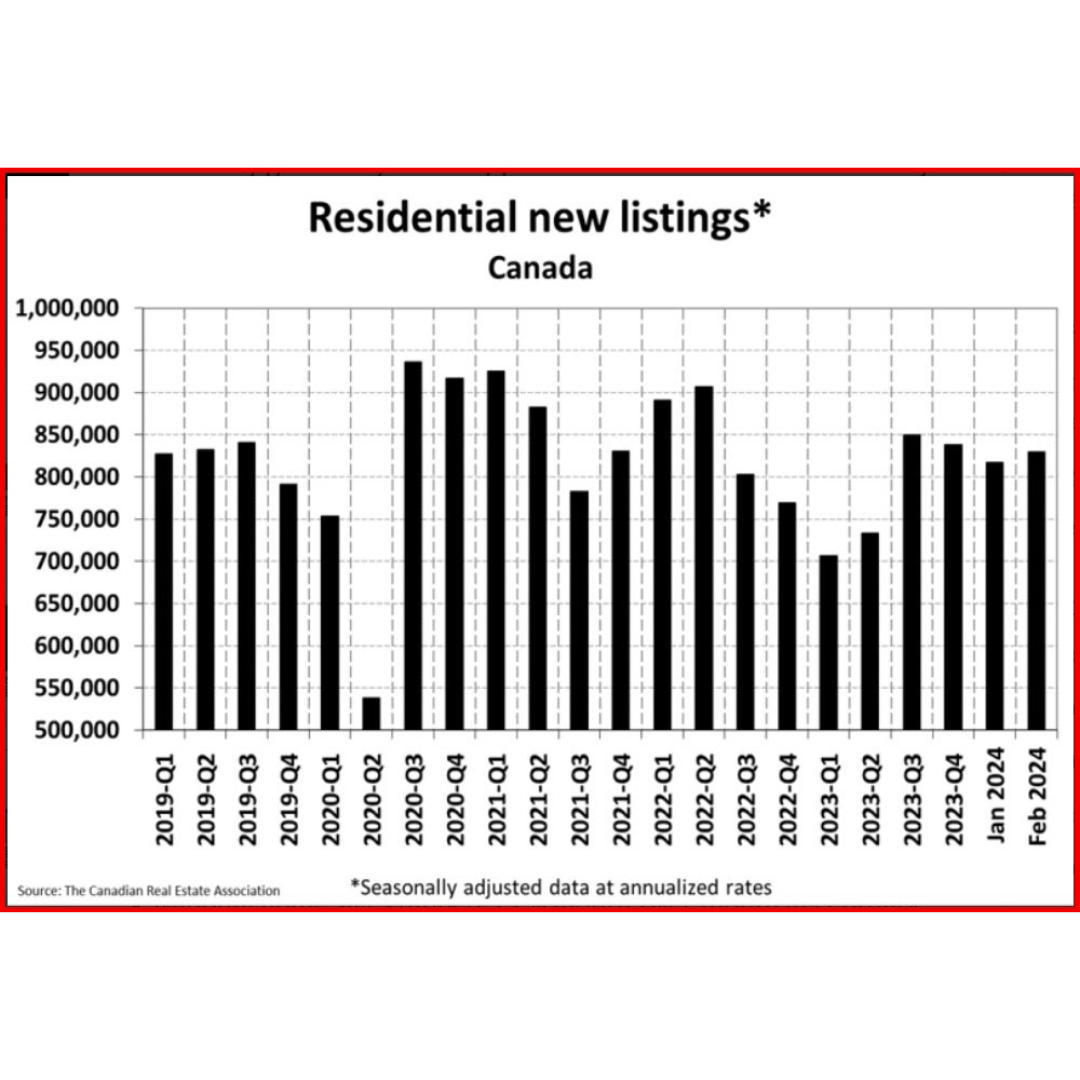
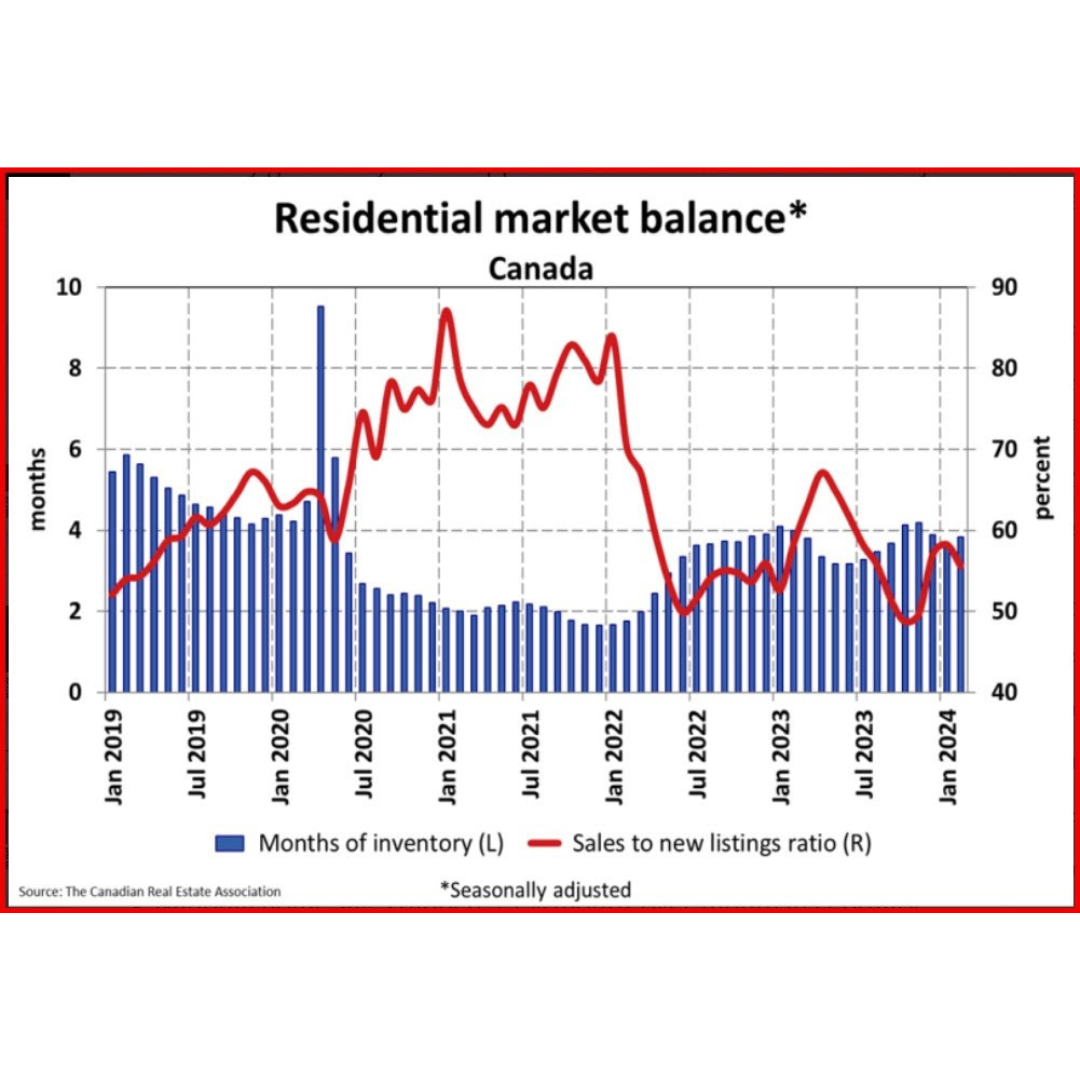
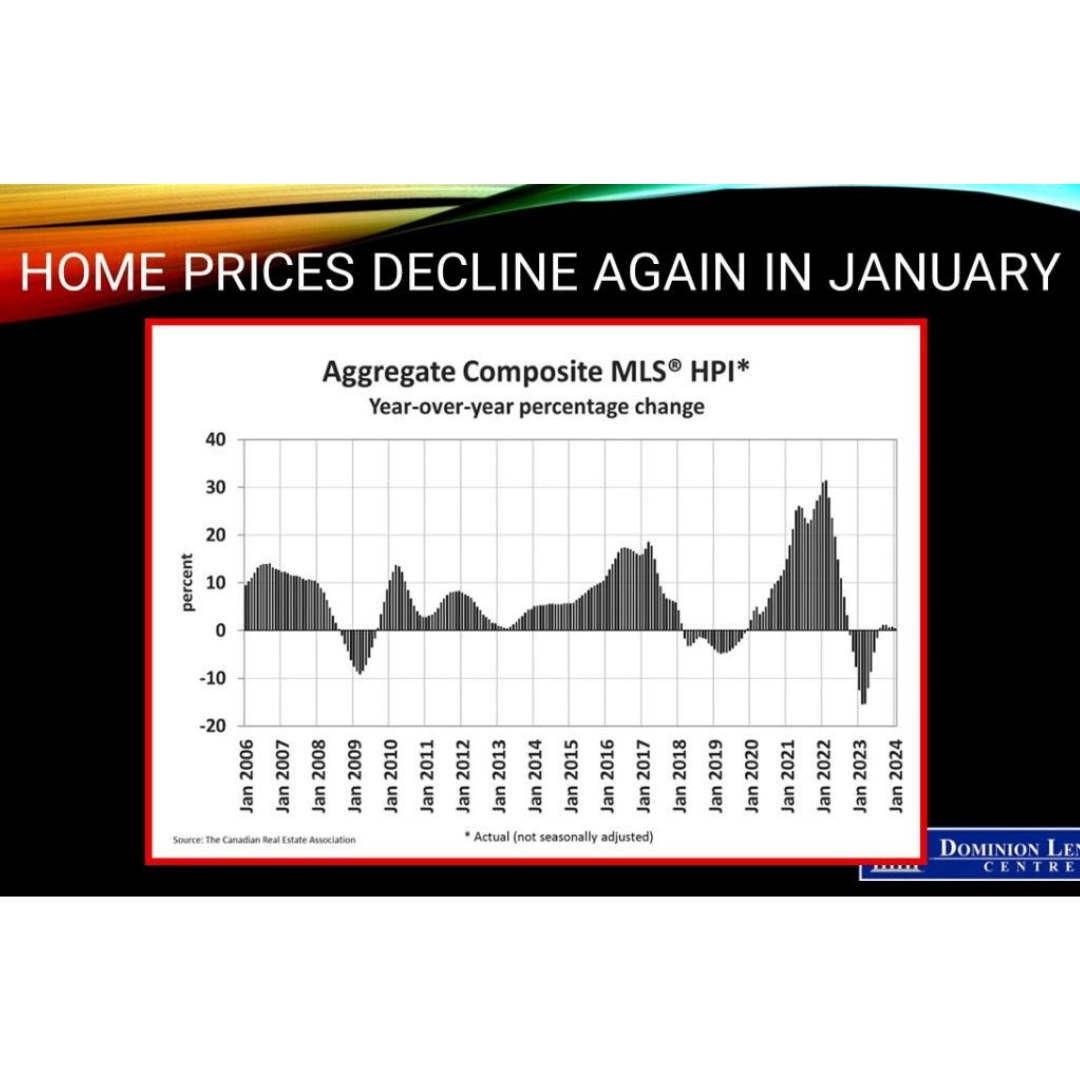
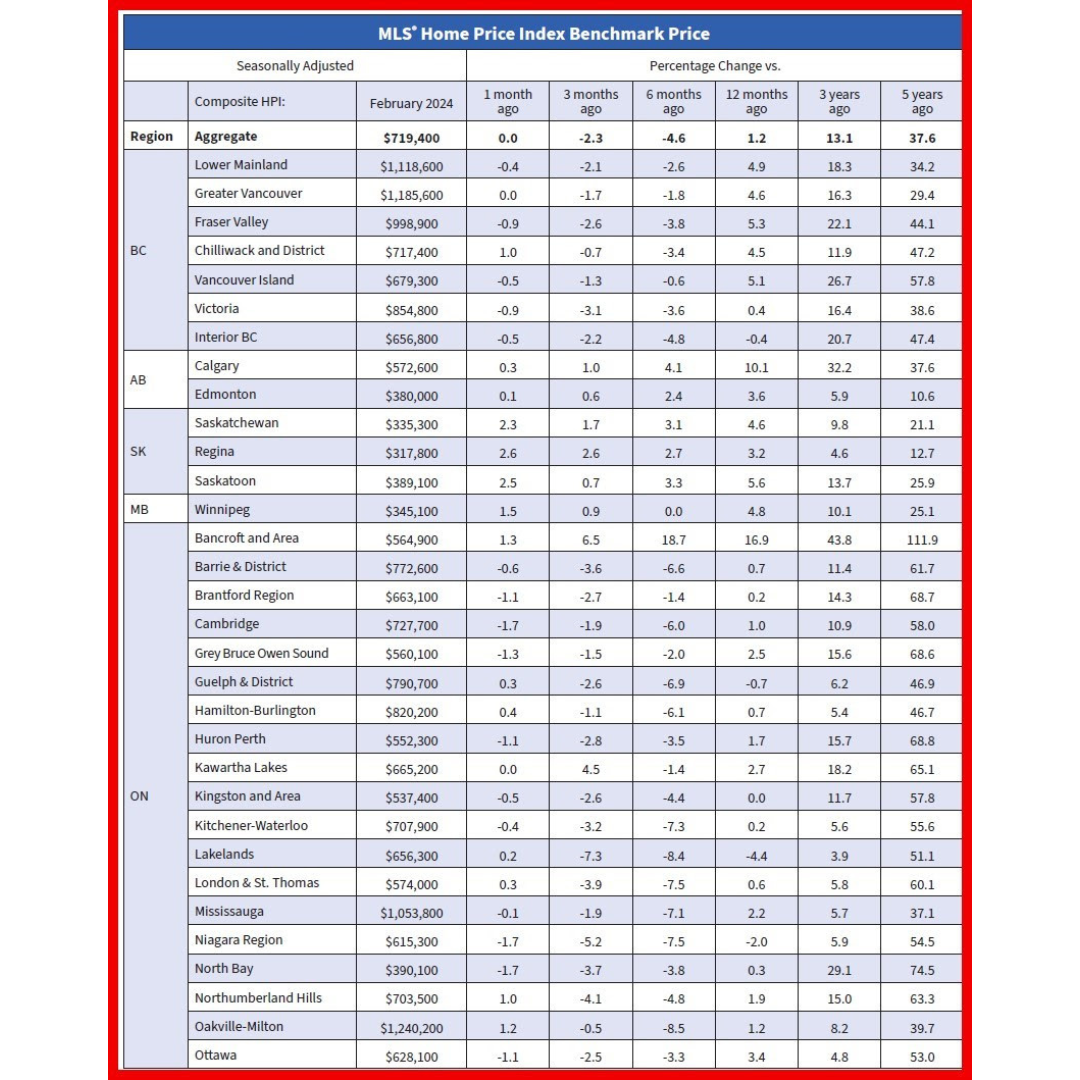
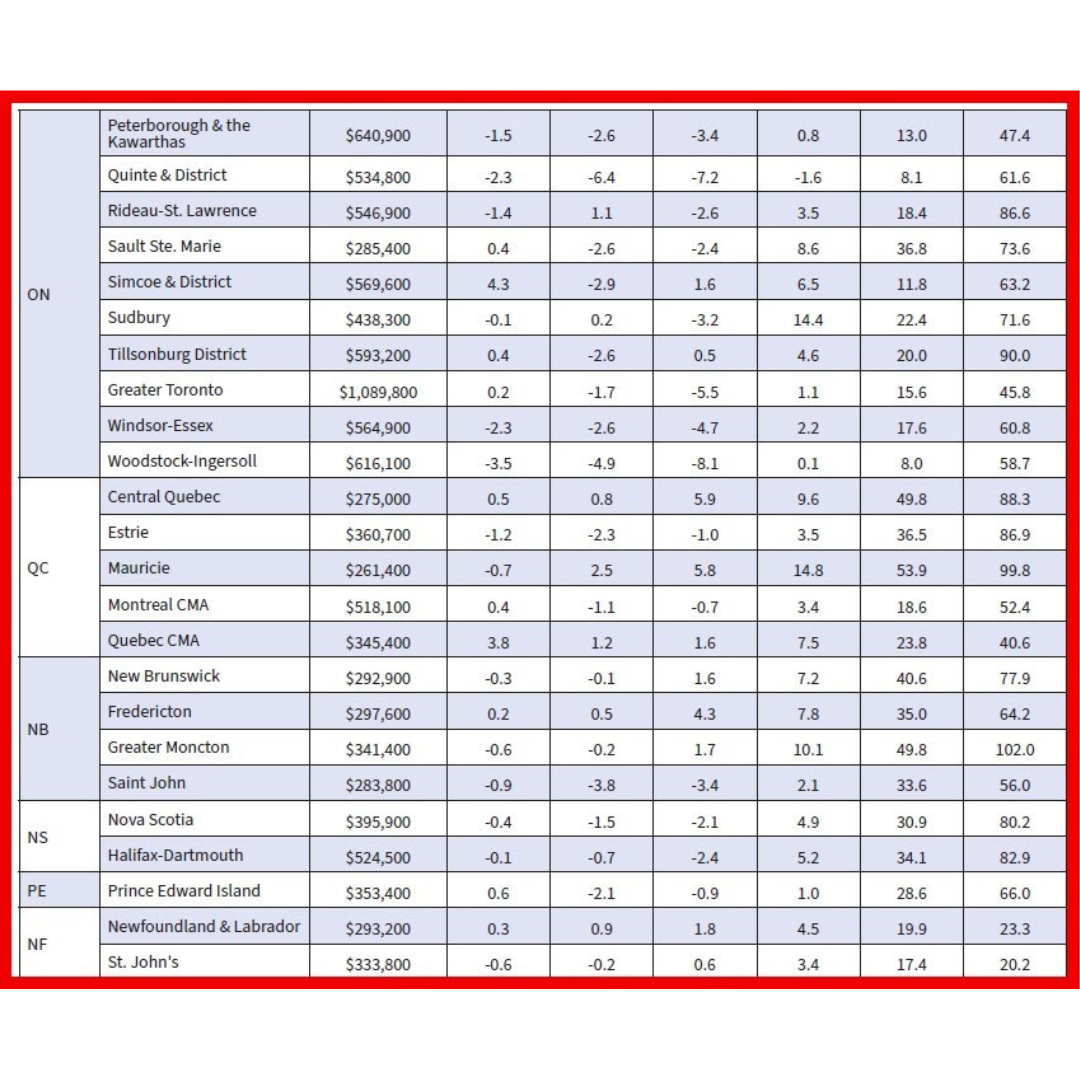
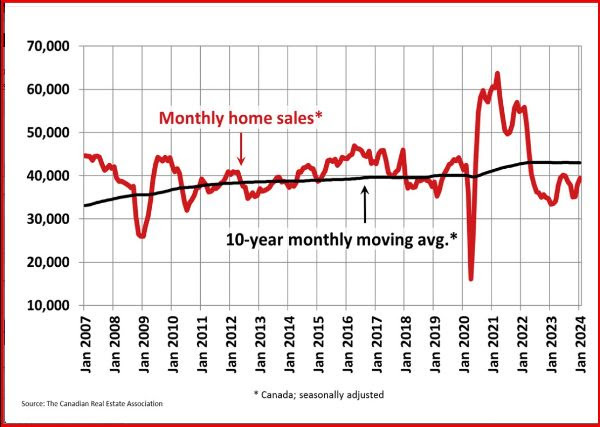
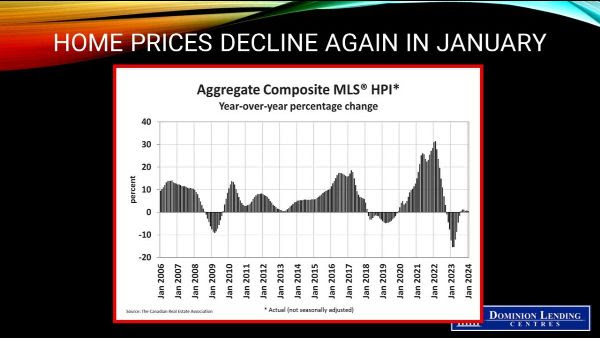
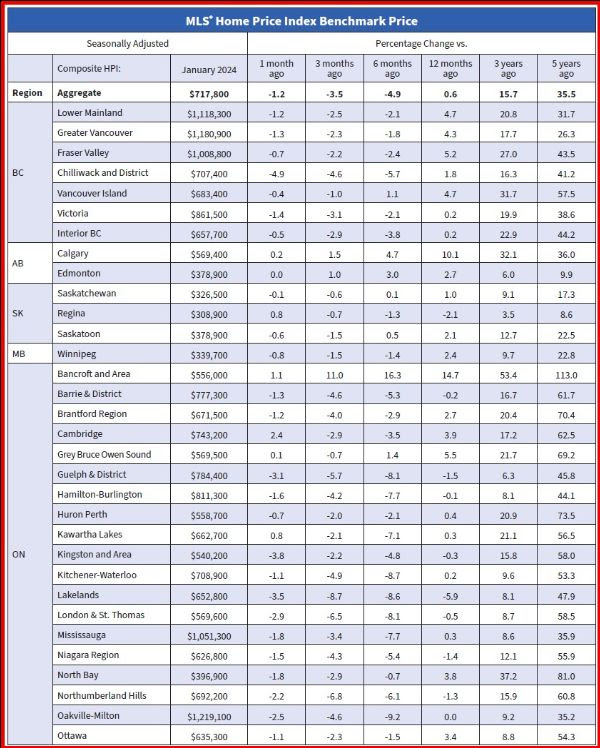
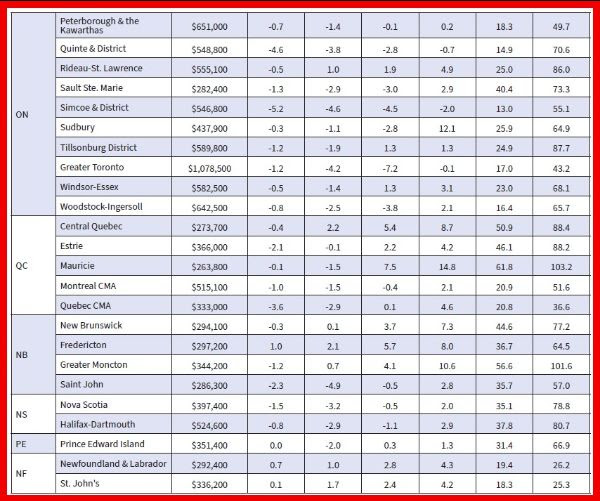
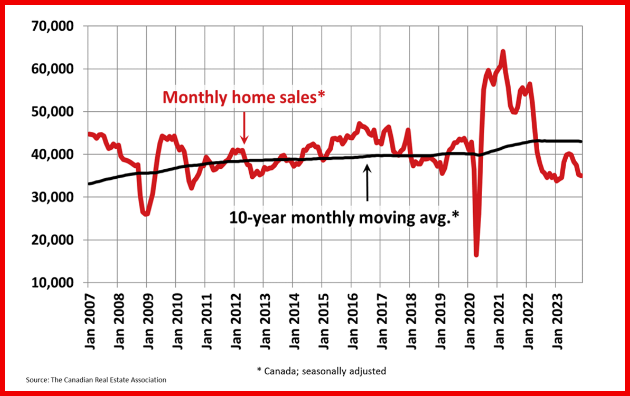
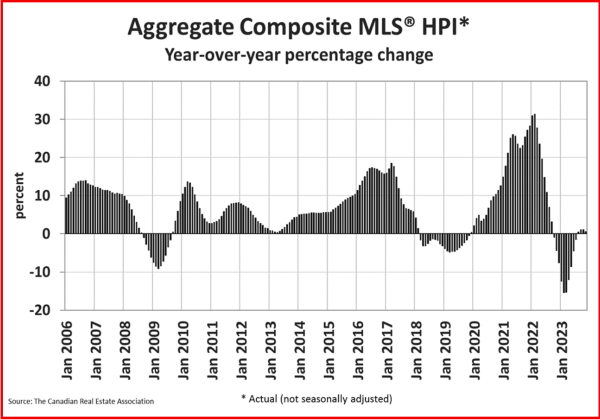
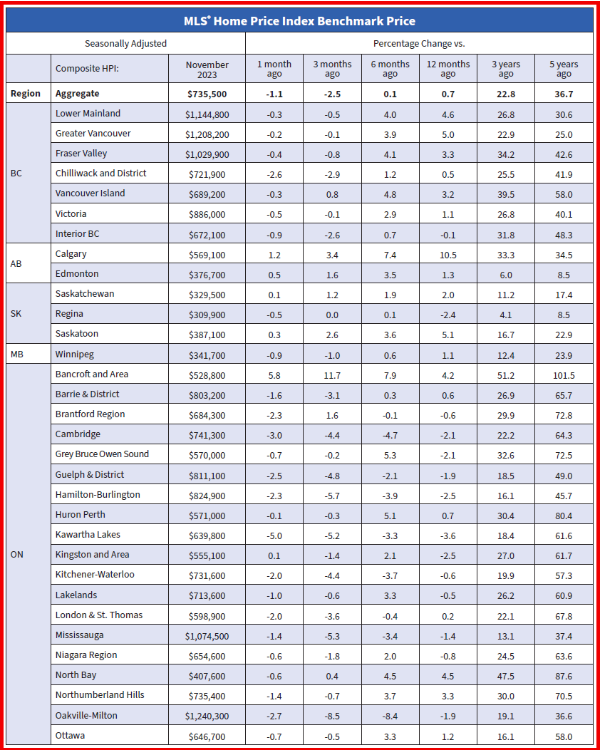
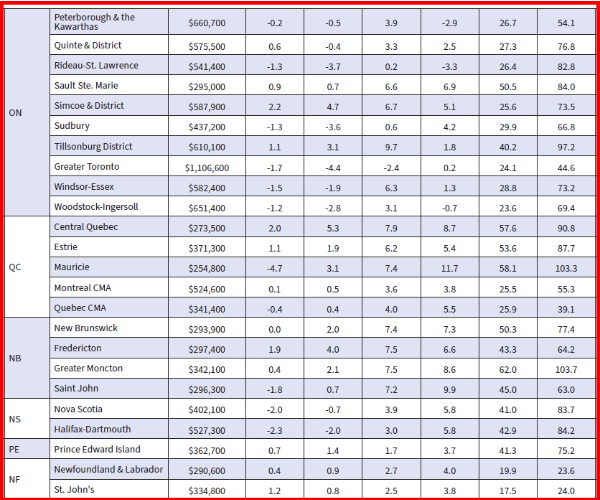
Resale activity picked up in Q1, driving the rise in housing investment, while new construction was flat. Ontario, British Columbia and Quebec posted the most significant volume increases in resales, while prices in these provinces fell in the first quarter.
New housing construction (+0.1%) was little changed in the first quarter, as work put in place decreased for all dwelling types except double houses. Costs related to new construction, such as taxes and closing fees upon change in ownership, increased in the quarter and were mainly attributable to newly absorbed apartment units in Ontario.
The household savings rate reached 7.0% in the first quarter, the highest rate since the first quarter of 2022, as gains in disposable income outweighed increases in nominal consumption expenditure. Income gains were derived mainly from wages and net investment income.
Investment income grew strongly in the first quarter of 2024 due to widespread gains from interest-bearing instruments and dividends. Higher-income households benefit more from interest rate increases through property income received.
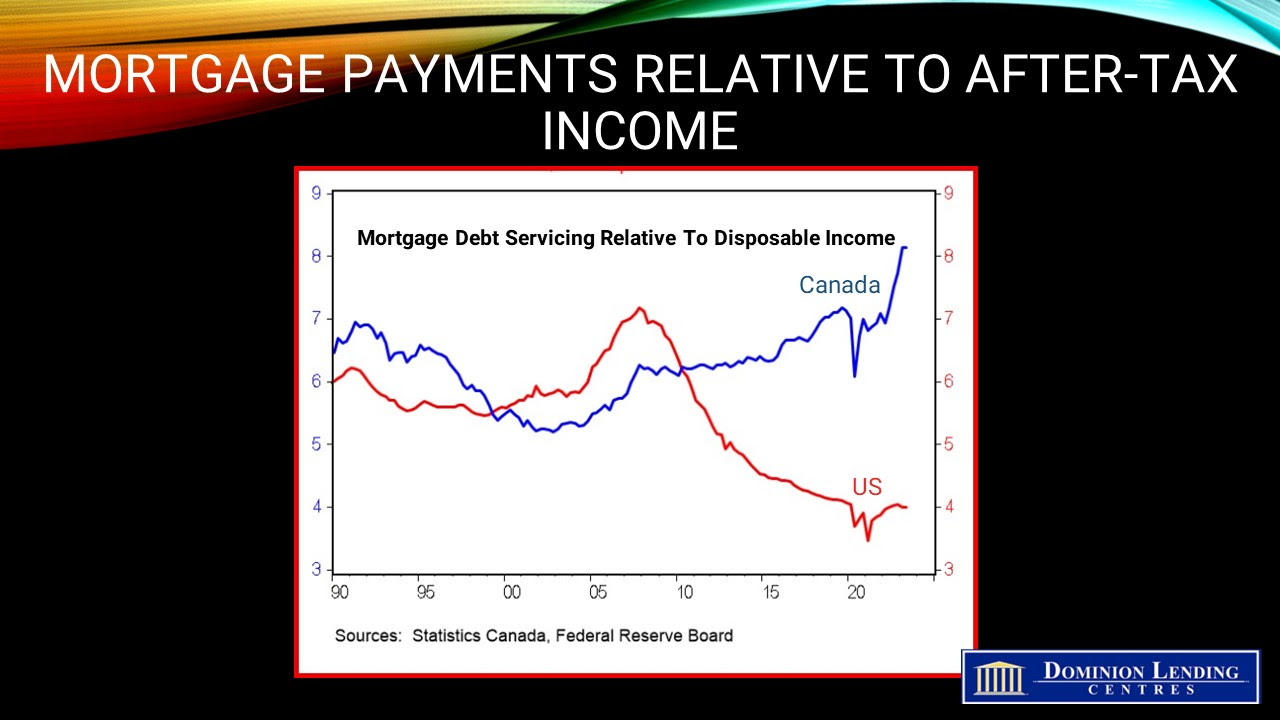
Household property income payments, comprised of mortgage and non-mortgage interest expenses, posted the lowest increases since the first quarter of 2022, when the Bank of Canada’s policy rate increases began.
Bottom Line
This is the last major economic release before the Bank of Canada meets again on June 5. Traders in overnight markets put the odds of a rate cut at next week’s meeting at about 75%, up from 66% the day before. Bonds rallied, and the yield on the Canadian government two-year note fell sharply, reflecting this change in sentiment.
The Bank of Canada has good reason to cut the overnight policy rate next week. Core inflation measures have decelerated sharply in recent months, and the economy is growing at a much slower pace than the central bank expected. The Bank has been very cautious, and there remains the possibility that they will wait another month before pulling the trigger on rate cuts, but at this point, we see no reason to delay any further.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres