May Was Another Sleepy Month For Housing
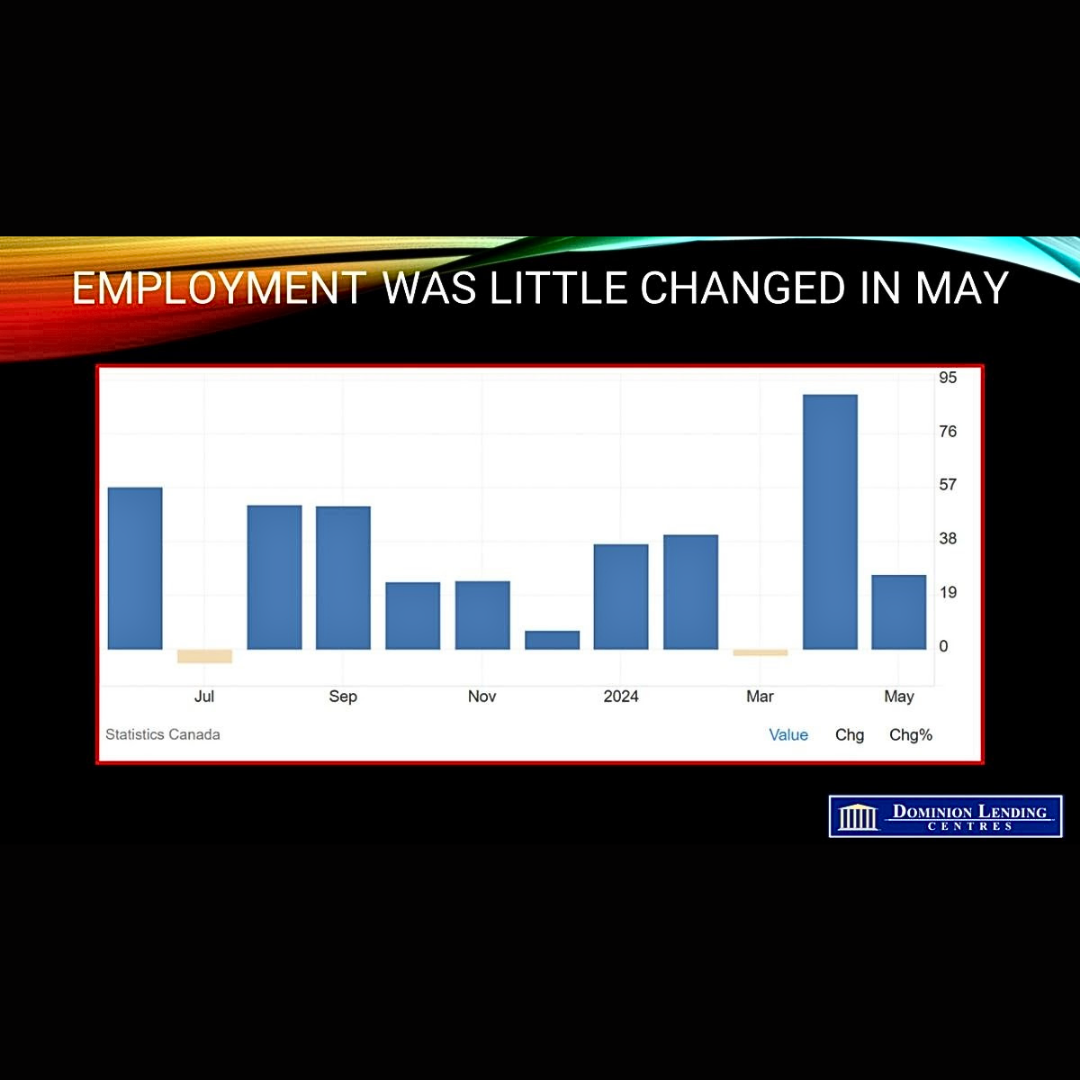
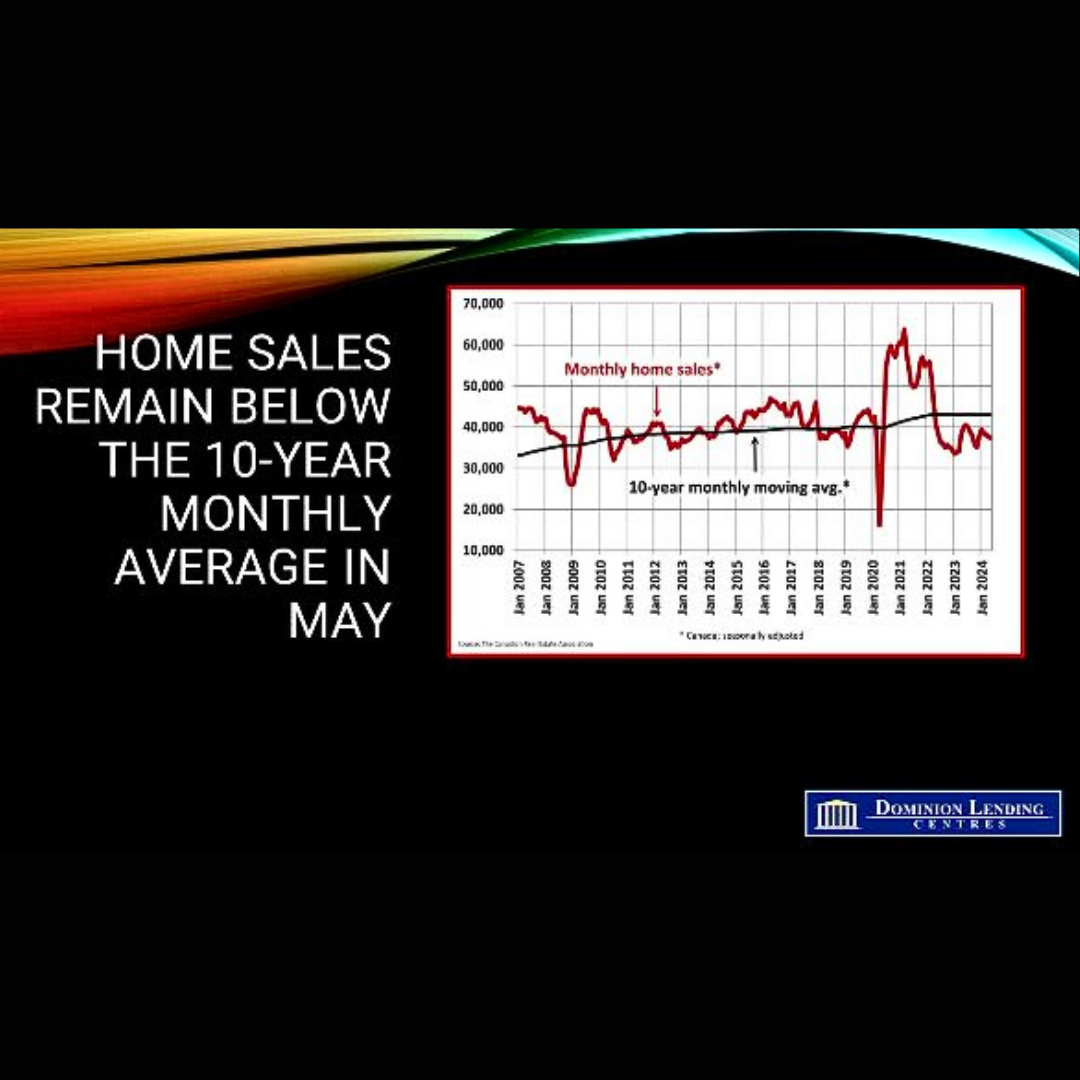
The Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA) announced today that national home sales fell 0.6% in May, remaining slightly below the average of the past ten years. Actual (not seasonally adjusted) monthly activity was 5.9% below May 2023.
With the Bank of Canada rate cut on June 5, housing activity will likely perk up in the coming months. The central bank will likely reduce the overnight policy rate from 4.75% to 3.0% by the end of next year. While interest rates will remain above pre-pandemic levels, there is pent-up demand for housing, and activity will surely rise over the next year
New Listings
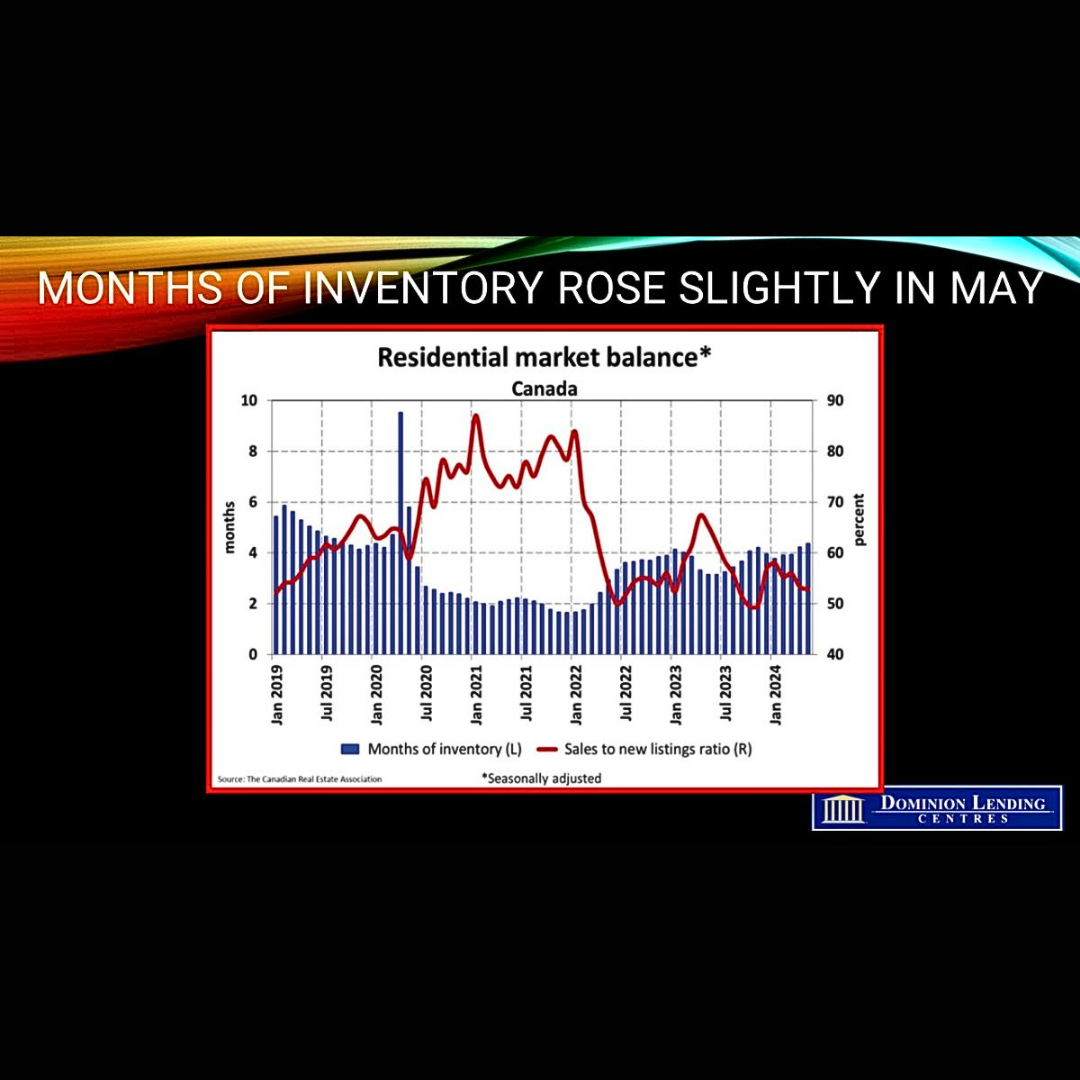
The number of newly listed homes was up in May, though only by 0.5% monthly. Slower sales amid more new listings this year have increased the number of homes for sale across most Canadian housing markets.
As of the end of May 2024, about 175,000 properties were listed for sale on all Canadian MLS® Systems, up 28.4% from a year earlier but still below historical averages.
“The spring housing market usually starts before all the snow has melted, somewhere around the beginning of April, but this year I believe a lot of people were waiting for the Bank of Canada to wave the green flag,” said James Mabey, Chair of CREA. “That first rate cut is expected to bring some pent-up demand back into the market, and those buyers will find there are more homes to choose from right now than at any other point in almost five years.”
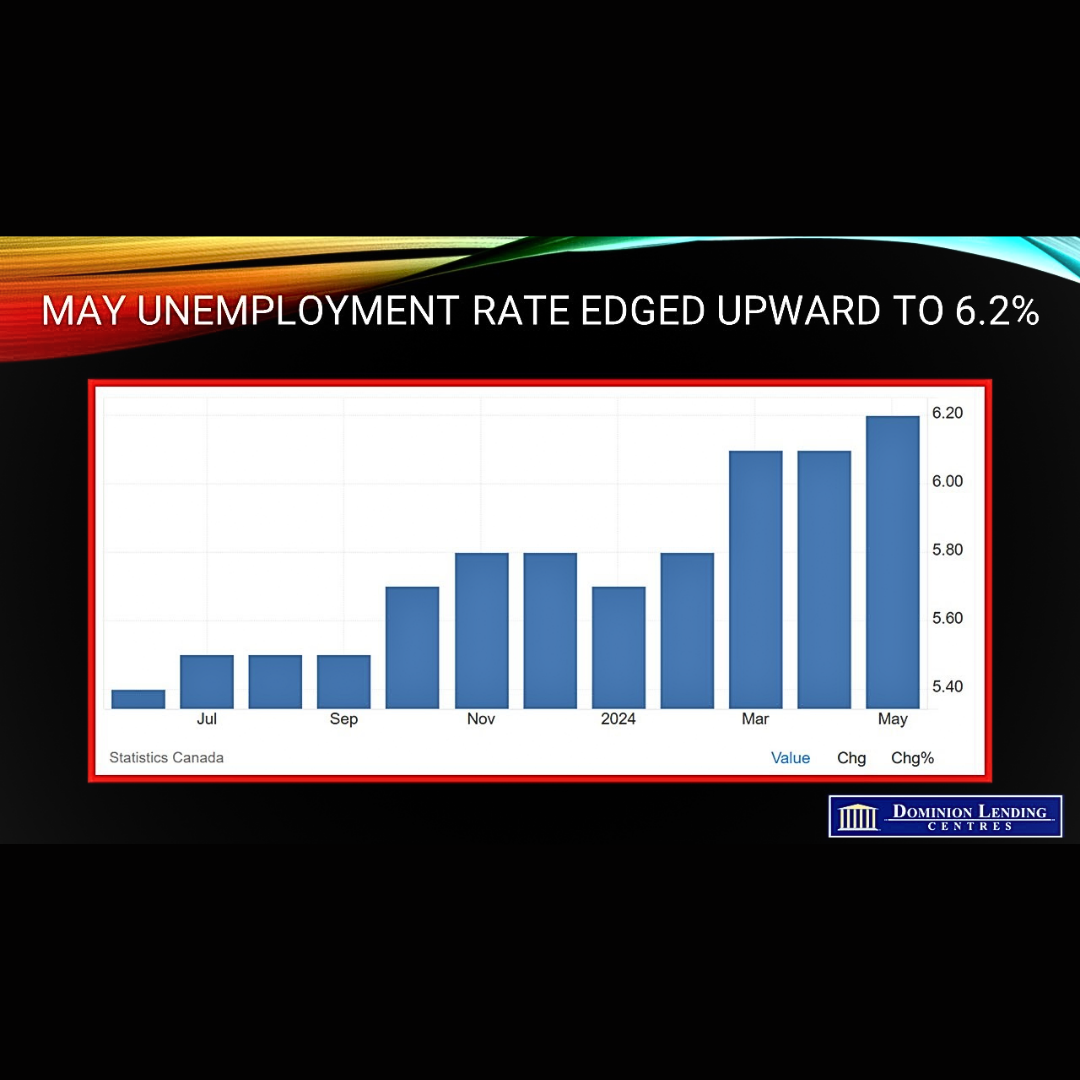
With sales down slightly and new listings up slightly in May, the national sales-to-new listings ratio eased to 52.6% compared to 53.3% in April. The long-term average for the national sales-to-new listings ratio is 55%. A sales-to-new listings ratio between 45% and 65% is generally consistent with balanced housing market conditions. There were 4.4 months of inventory on a national basis at the end of May 2024, up from 4.2 months at the end of April and, looking past the volatility at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the highest level for this measure since the fall of 2019. The long-term average is about five months of inventory.

Home Prices
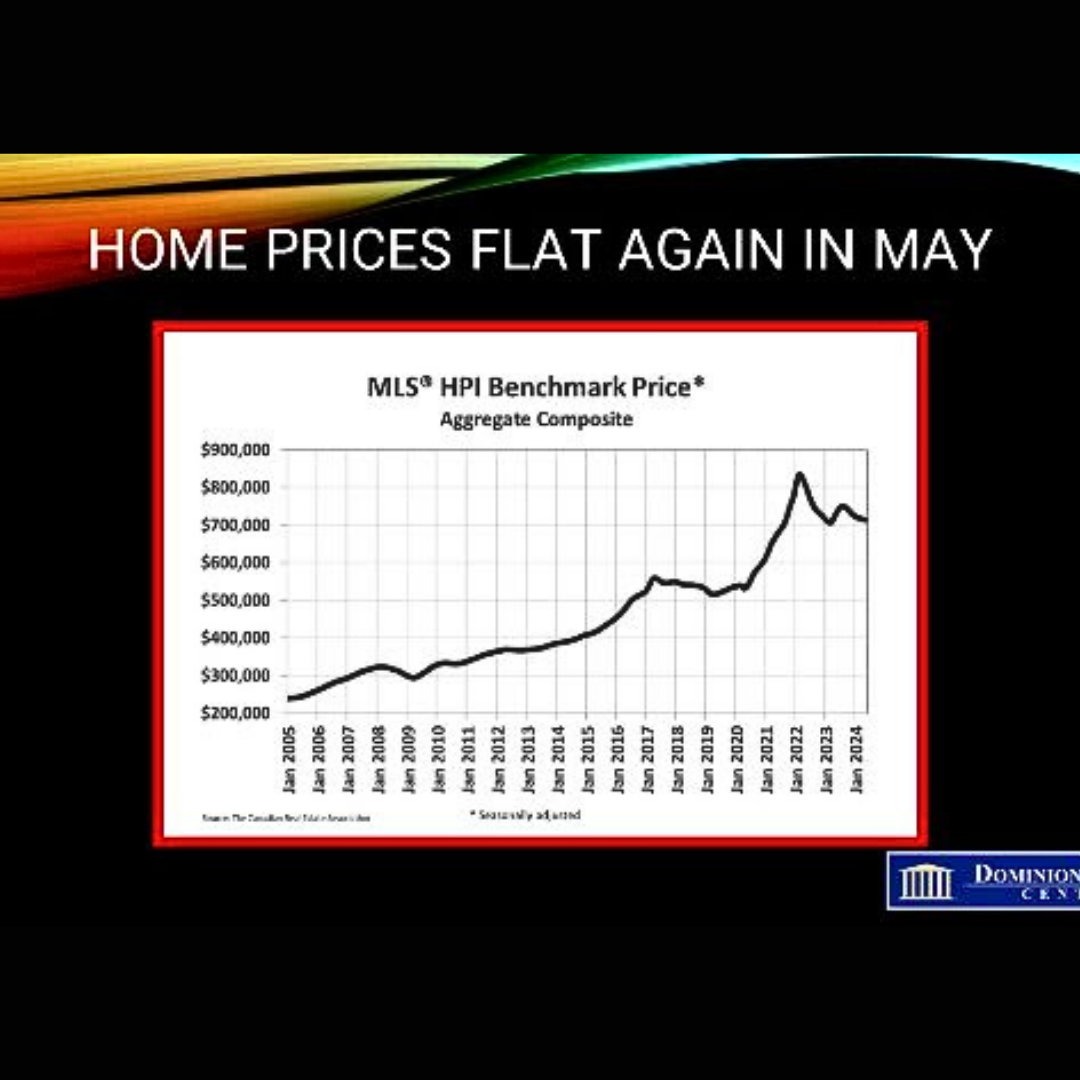
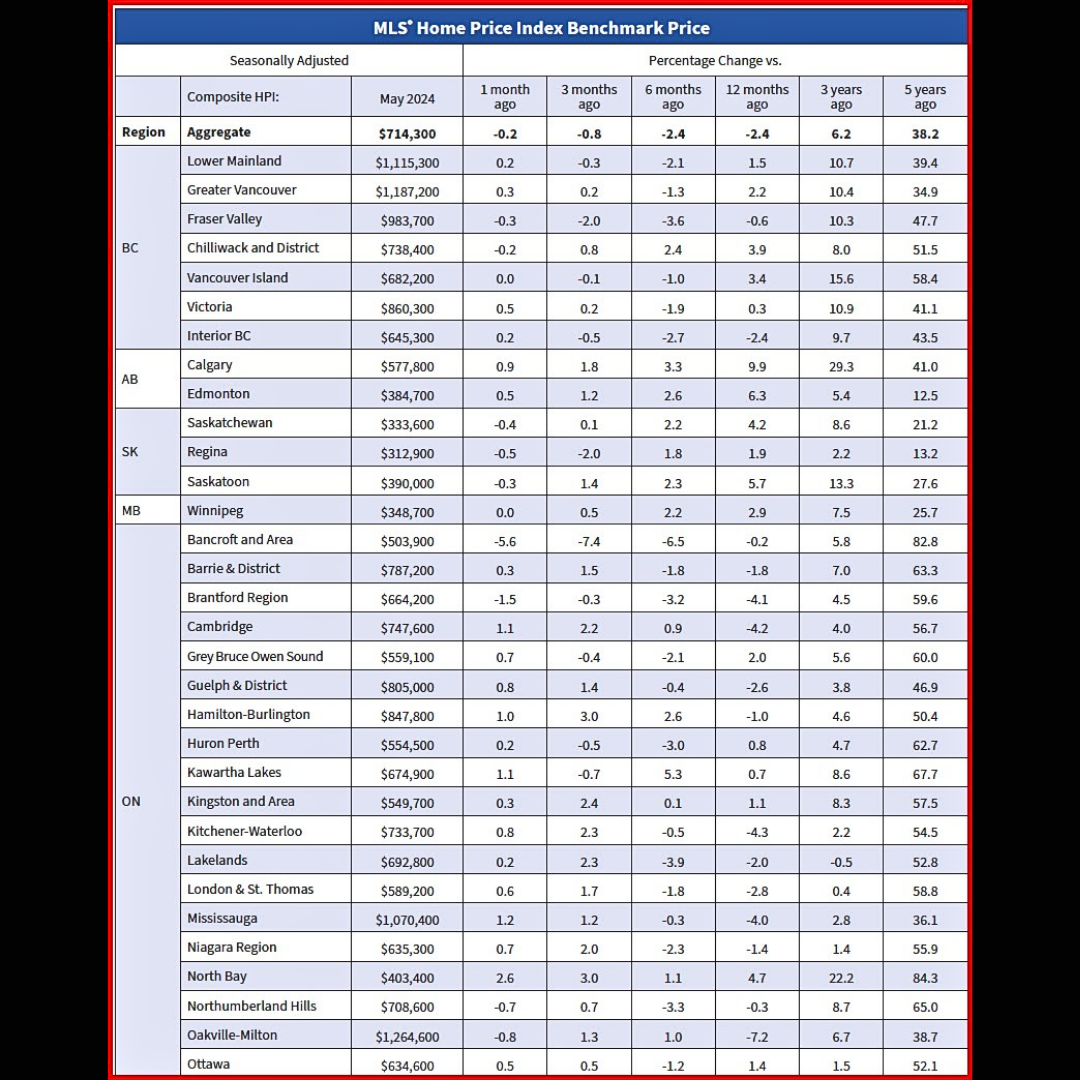
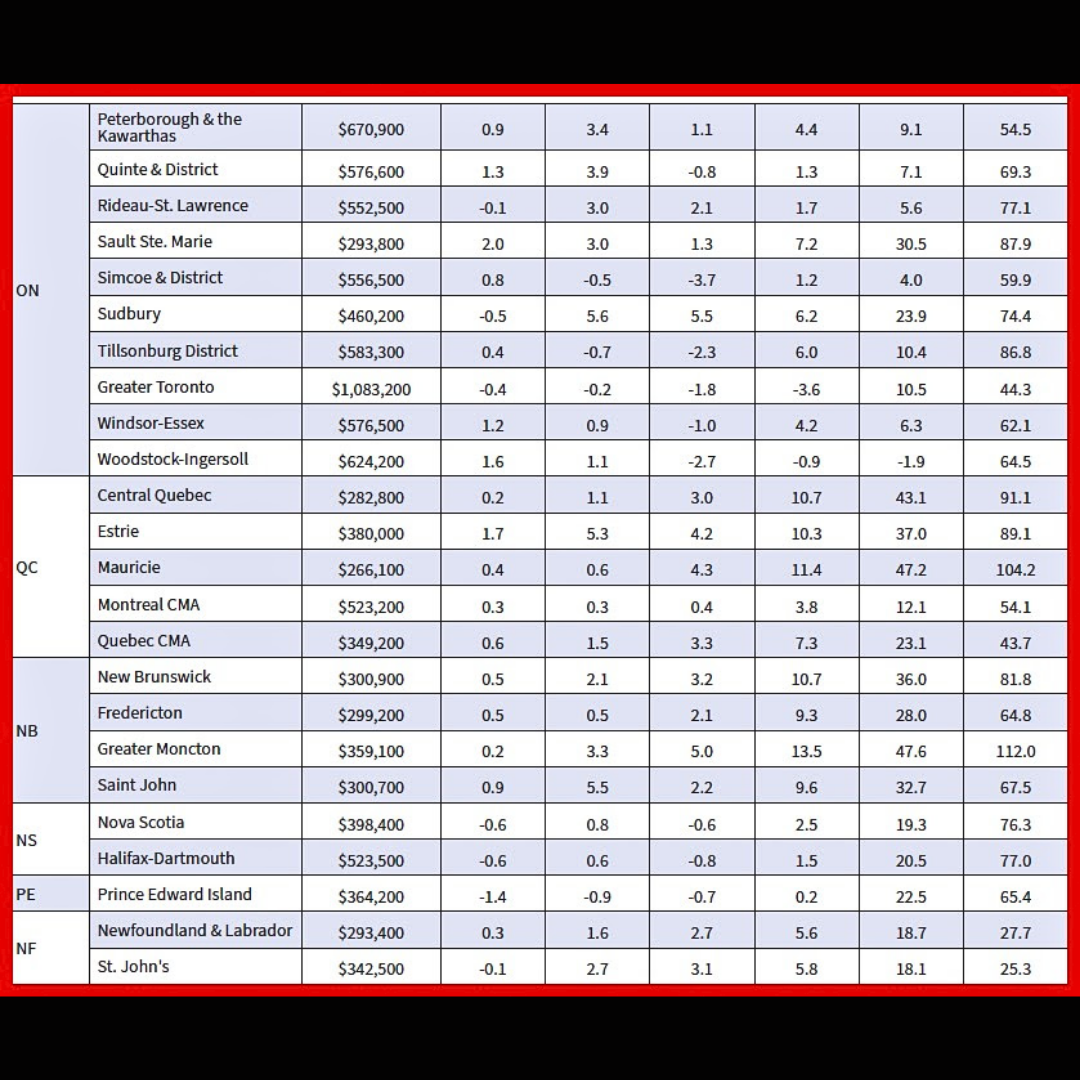
The National Composite MLS® Home Price Index (HPI) dipped 0.2% from April to May.
Regionally, prices are generally sliding sideways across most of the country. The exceptions remain Calgary, Edmonton, and Saskatoon, where prices have steadily ticked higher since the beginning of last year.
The non-seasonally adjusted National Composite MLS® HPI stood 2.4% below May 2023. This mostly reflects the price surge that started last April and hasn’t been repeated in 2024.
Bottom Line
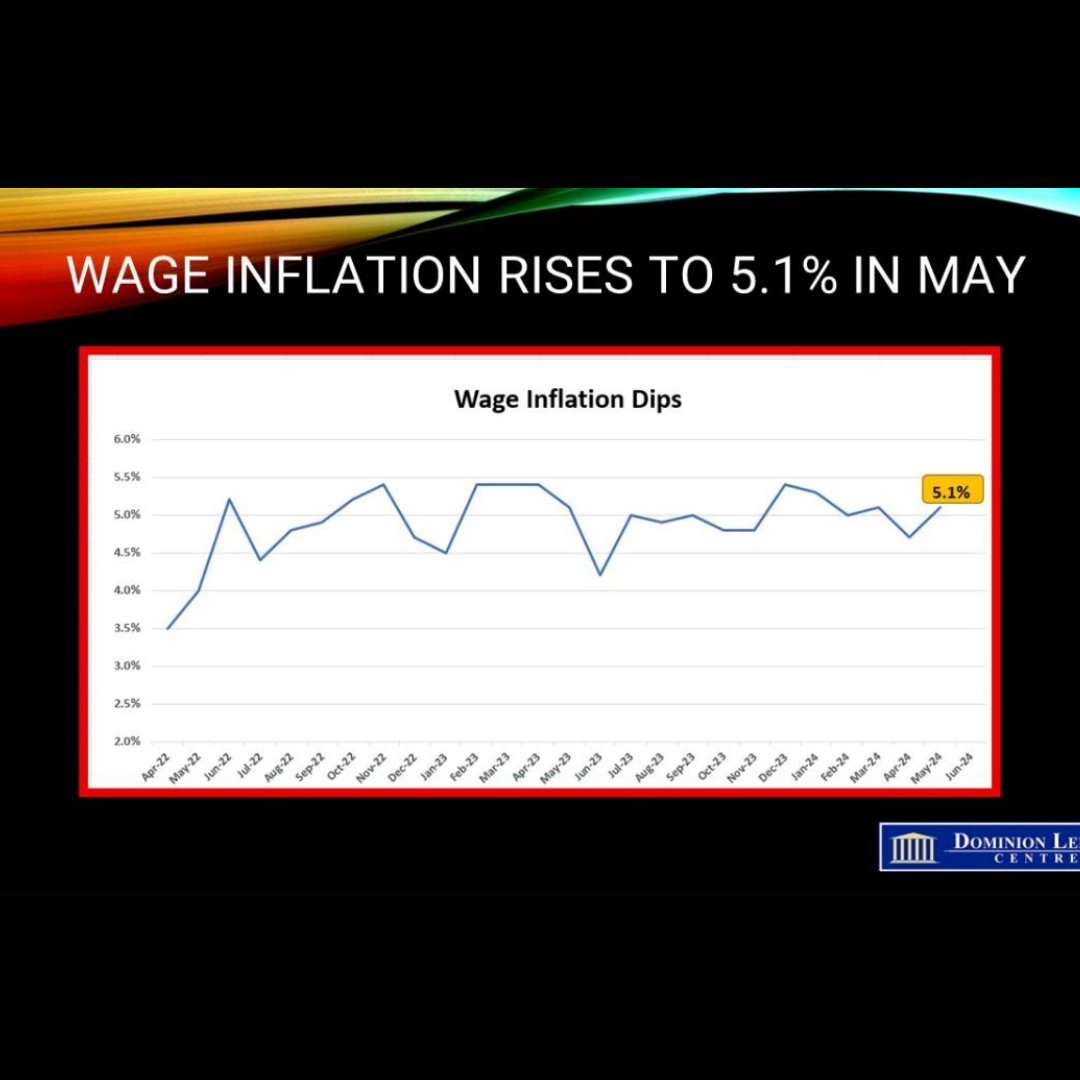
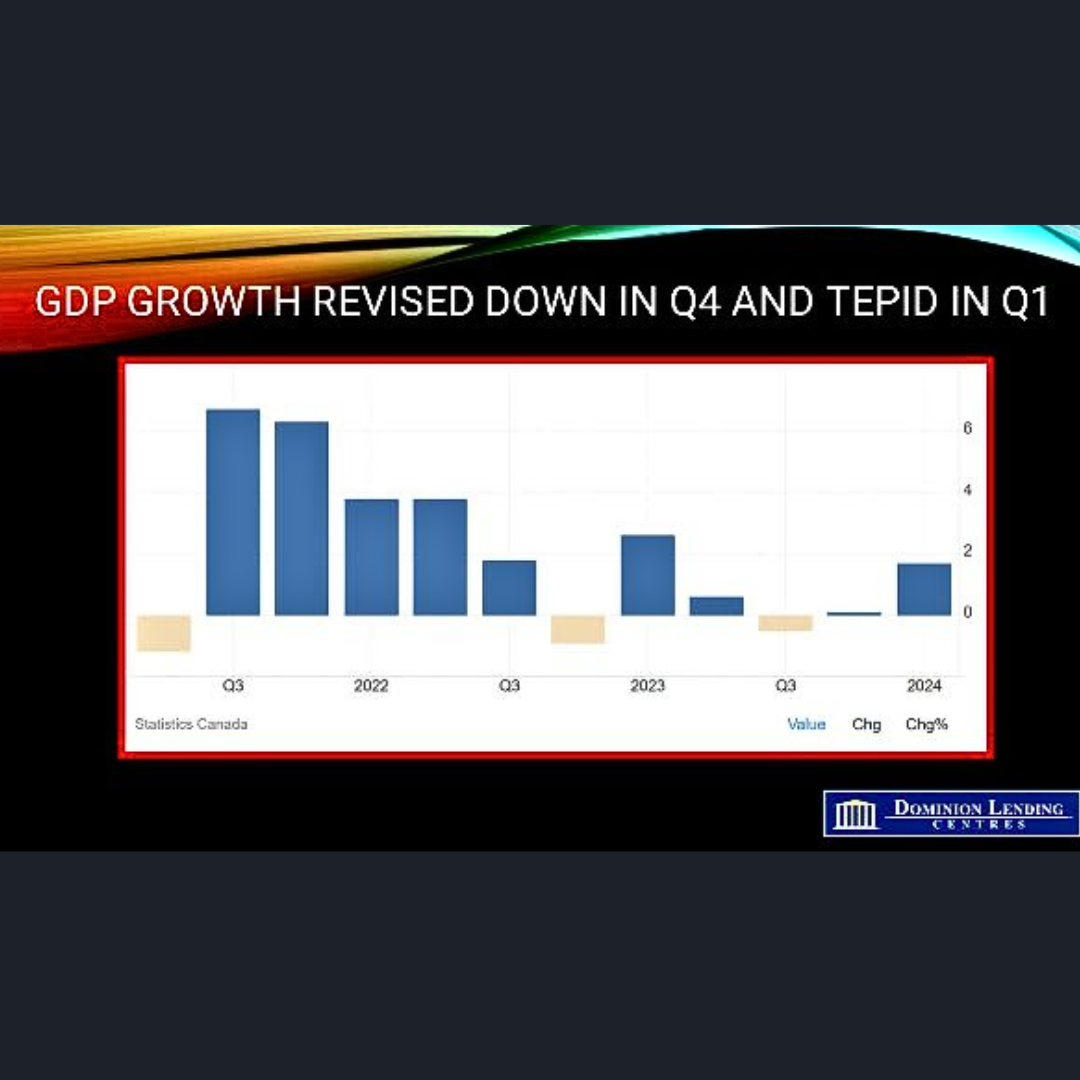
Housing activity will gradually accelerate over the next year as interest rates continue to fall. The Bank of Canada was the first major central bank to ease monetary policy. While there has been some concern regarding the impact on the Canadian dollar of repeated easing by the Bank with the US Federal Reserve on hold, the divergence may be smaller than expected. Recent US inflation data showed a meaningful improvement, suggesting the Fed could cut rates two times before the end of the year. Moreover, movements in the loonie have little near-term impact on inflation.
The Canadian economy is far more interest-sensitive than the US, and the relative underperformance of our economy is the largest since 1965. Further rate cuts by the Bank of Canada are warranted.
Source: Dr. Sherry Cooper, Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres